 Figure 1: Diagram and list of components of the Flashlight. To light a high brightness LED with a 1.5V battery, we have raised the battery voltage with a small DC DC converter step-up consists of two transistors and two PNP ZTX653-JAF2 JAF1 coils in parallel.
Figure 1: Diagram and list of components of the Flashlight. To light a high brightness LED with a 1.5V battery, we have raised the battery voltage with a small DC DC converter step-up consists of two transistors and two PNP ZTX653-JAF2 JAF1 coils in parallel. An LED is a nonlinear component needing to power a higher voltage than its power of conduction, so that the current used to enlightenment can flow through the junction.
Take an ordinary red LED whose conduction voltage is 1.8 V, and if we feed it at 1.5 V it will not light because it lacks 0.3 V for the voltage threshold conduction is reached . Each LED color is a threshold voltage conduction different, here's a preview:
TABLE 1

By changing the forward voltage can, within limits, to vary the brightness: the higher the current passing through it is more intense LED lights up (but be careful not to exceed the current breakdown of the junction is ie the power dissipation).
To light a red LED we normally use at least two 1.5V batteries connected in series, making a complex voltage of 3 V and you go, always in series, for example in the + supply, a resistor current limit. If you want to be prudent to limit this to 15 mA forward current is applied the following formula to calculate the value of the limiting resistor R:
where R is in ohms, Vcc supply voltage V, VLED the conduction voltage V, I, the maximum current that we want to bear in mA to the LED, this gives:
Higher voltages are needed to illuminate the white or blue LEDs with high brightness, as their conduction voltage is about 3 V (see Table 1).
As for the red LEDs, we would normally use a power source greater than this value, not to mention limiting resistor (so the current through the LED is about 20-30 mA maximum).
This time we climb three 1.5 V batteries in series for a Vcc of 4.5 V and we get into a series limiting resistor of 82 ohms or 100, depending on the brightness that we want.
But sometimes this solution can not be adopted because there was only room for one battery of 1.5 V.
Then we must raise the voltage to exceed the conduction voltage of the LED used. That's what we did in the circuit in Figure 1 which shows the wiring diagram.
If you want to power a LED whose threshold conduction voltage is 3 V (case of a high brightness white LED) with a 1.5 V battery, we need to make a small DC-DC step- up "(also called" Booster ") capable of providing a voltage above this threshold. For this, we mounted two NPN transistors ZTX653 (TR1-TR2).
They were chosen because they have a VCEsat (Vce saturation) very low and because they are designed for low voltage power supplies.
Note: VCEsat is the voltage Vce saturation voltage is between C and E when the transistor conducts (saturation).
In low voltage applications it is preferable to have the lowest value of Vce possible because it improves the efficiency of the converter.
They form an oscillator at about 90 kHz. This frequency is determined by the coils (standard, do not worry!) JAF1-JAF2 connected in parallel (inductive value divided by two, but maximum permissible current multiplied by two) and the ceramic capacitor C1 feedback.
The voltage signal present on the square collector of TR2 is stored in the two reactors of 110 uH (inductive total value of the two in parallel), this energy (Ton) is then transferred to the LED (Toff) as a voltage greater than the supply voltage.
Note: this is the principle of switching power supplies "step-up/boost.
As the conduction voltage of the LED is exceeded, the current can move and turn the junction of the LED light up as we see constantly in the phenomenon of persistence of vision, then it turns on and off 90 000 times per second!
No-limiting resistor is no longer necessary because the current supplied is not significant and limited by the characteristics of inductors 15 or 20 mA, which is more than enough to brighten up two LEDs in parallel.
But of course you know us, we could not bring ourselves to stop there! If possession of an LED flashlight powered by a battery of 1.5 V does not interest you and if you prefer the "idea" of the small switching power supply DC-DC lift, well you get satisfaction. The voltage depends on the current drawn by the load, as shown in Table 2 below:
TABLE 2
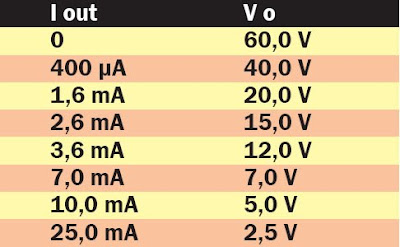
With a single 1.5 V battery can power this circuit the tuning circuit of an FM radio at low voltage because it can feed its varactor diodes, or any circuit using operational.
Whatever the route chosen (torch or power) you'll have no trouble building it.
 Figure 2: Photograph of a prototype of the plate Flashlight EN1664 with his cell door (cell stick miniature 1.5 V). The LED is inserted and welded after it has folded its legs to 90 degrees.
Figure 2: Photograph of a prototype of the plate Flashlight EN1664 with his cell door (cell stick miniature 1.5 V). The LED is inserted and welded after it has folded its legs to 90 degrees. Iist EN1664
R1 ....... 2.2 kO
R2 ....... 1 kO
R3 ....... 1 kO
C1 ...... 470 pF ceramic
C2 ...... 100 uF electrolytic
JAF1 .... 220 uH
JAF2 .... 220 uH
DL1 ..... Flash LED (High brightness)
TR1 ..... NPN ZTX653
TR2 ..... NPN ZTX653
P1 ...... push
Unless otherwise specified, all resistors are 1 / 4 W 5%.



1 comment:
What are the best free online casinos for making money? - Work
What are the best free online casinos for making money? · Top Casino List · BetUS หาเงินออนไลน์ · Rake.io · 888casino · 888casino.
Post a Comment